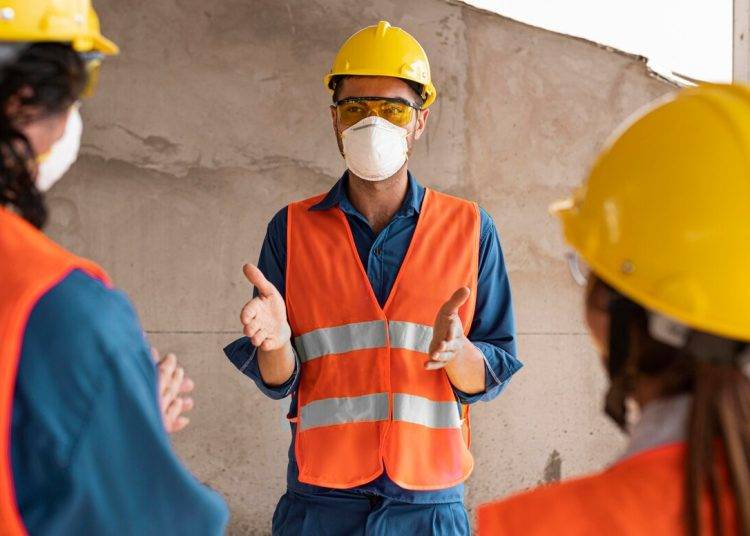
Workplace safety is a fundamental aspect of any organization, transcending mere compliance with regulations and legal obligations. It encompasses the well-being of employees, the protection of assets, and the overall efficiency of operations. A safe work environment not only reduces the risk of accidents and injuries but also fosters a culture of trust and respect among employees.
When workers feel secure in their surroundings, they are more likely to be productive, engaged, and committed to their roles. This sense of security can lead to lower turnover rates, as employees are less inclined to seek employment elsewhere when they feel valued and protected. Moreover, the financial implications of workplace safety cannot be overstated.
Organizations that prioritize safety often experience reduced costs associated with workplace injuries, such as medical expenses, workers’ compensation claims, and lost productivity. For instance, the National Safety Council estimates that workplace injuries cost U.S. employers over $170 billion annually.
By investing in safety measures, such as Australian safety mats, companies can mitigate these costs significantly. Additionally, a strong safety record can enhance a company’s reputation, making it more attractive to potential clients and customers who prioritize corporate responsibility. In this way, workplace safety is not just a moral obligation; it is a strategic business decision that can yield substantial returns.
Creating a Safety Culture
Establishing a safety culture within an organization requires a concerted effort from all levels of management and staff. It begins with leadership demonstrating a genuine commitment to safety through their actions and policies. When executives prioritize safety in their decision-making processes and allocate resources towards safety initiatives, it sends a powerful message to employees about its importance.
This commitment should be reflected in the organization’s mission statement and core values, ensuring that safety is woven into the fabric of the company’s identity. In addition to leadership commitment, employee involvement is crucial in fostering a safety culture. Organizations can encourage this by creating platforms for open communication where employees feel comfortable voicing their concerns about safety issues without fear of retribution.
Regular safety meetings and workshops can serve as forums for discussing potential hazards and sharing best practices. Furthermore, recognizing and rewarding safe behavior can motivate employees to take ownership of their safety responsibilities. For example, implementing a “safety champion” program where employees are acknowledged for their contributions to workplace safety can enhance engagement and accountability.
Identifying and Mitigating Hazards
The process of identifying and mitigating hazards is an ongoing endeavor that requires vigilance and proactive measures. Organizations must conduct thorough risk assessments to pinpoint potential dangers in the workplace. This involves evaluating the physical environment, equipment, and work processes to identify anything that could pose a risk to employee safety.
For instance, in a manufacturing setting, this might include assessing machinery for proper guarding or evaluating the layout of the workspace to ensure safe movement and access. Once hazards are identified, organizations must implement strategies to mitigate these risks effectively. This could involve engineering controls, such as installing safety guards on machines or improving ventilation systems to reduce exposure to harmful substances.
Administrative controls, including modifying work schedules or implementing job rotation to minimize repetitive strain injuries, are also essential. Personal protective equipment (PPE) plays a critical role in hazard mitigation as well; providing employees with appropriate gear such as helmets, gloves, or respirators can significantly reduce the likelihood of injury or illness. Continuous monitoring and reassessment of hazards are vital to ensure that mitigation strategies remain effective as work conditions evolve.
Training and Education
Training and education are cornerstones of an effective workplace safety program. Employees must be equipped with the knowledge and skills necessary to recognize hazards and respond appropriately in emergency situations. Comprehensive training programs should cover various aspects of workplace safety, including proper equipment usage, emergency response procedures, and the importance of reporting unsafe conditions.
For example, in a construction environment, workers should receive training on fall protection measures, scaffolding safety, and the correct use of power tools. Moreover, training should not be a one-time event but rather an ongoing process that adapts to changes in the workplace or industry standards. Regular refresher courses can help reinforce safe practices and keep safety at the forefront of employees’ minds.
Incorporating hands-on training exercises allows employees to practice their skills in real-world scenarios, enhancing their confidence and preparedness. Additionally, organizations should consider utilizing technology such as virtual reality simulations for training purposes, which can provide immersive experiences that improve retention and understanding of safety protocols.
Regular Safety Inspections and Maintenance
Conducting regular safety inspections is essential for maintaining a safe work environment. These inspections should be systematic and thorough, examining all aspects of the workplace for compliance with safety standards and identifying any potential hazards that may have arisen since the last inspection. Inspections can be scheduled at regular intervals or conducted randomly to ensure that safety remains a priority at all times.
Engaging employees in these inspections can also foster a sense of ownership over workplace safety. Maintenance plays a critical role in ensuring that equipment and facilities remain safe for use. Regular maintenance schedules should be established for machinery, tools, and other equipment to prevent malfunctions that could lead to accidents.
For instance, in an industrial setting, failing to maintain machinery could result in breakdowns or unsafe operating conditions that endanger workers. Additionally, maintaining clear pathways and ensuring that emergency exits are unobstructed are vital components of workplace safety that should not be overlooked during inspections.
Reporting and Responding to Incidents
An effective incident reporting system is crucial for addressing workplace accidents and near misses promptly. Employees should be encouraged to report any incidents or unsafe conditions without fear of punishment or stigma. This open reporting culture allows organizations to gather valuable data on incidents that can inform future safety measures and training programs.
For example, if multiple employees report near misses related to a specific piece of equipment, management can investigate further and implement corrective actions before an actual injury occurs. Responding to incidents requires a well-defined protocol that outlines the steps to be taken following an accident or near miss. This includes providing immediate medical attention if necessary, conducting an investigation to determine the root cause of the incident, and implementing corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
Organizations should also analyze incident data regularly to identify trends or patterns that may indicate systemic issues within their safety practices. By taking these steps seriously, companies not only demonstrate their commitment to employee safety but also create an environment where continuous improvement is prioritized. In conclusion, workplace safety is an integral part of organizational success that requires ongoing commitment from all stakeholders involved.
By fostering a culture of safety, identifying hazards proactively, providing comprehensive training, conducting regular inspections, and responding effectively to incidents, organizations can create an environment where employees feel secure and valued. The benefits extend beyond compliance; they encompass enhanced productivity, reduced costs associated with injuries, and an overall positive workplace atmosphere that contributes to long-term success.